
What does diffraction imply but why does it occur?ĭiffraction is the expansion of waves when they pass through an aperture or around barriers. Image credit: Snappy goat Frequently asked question |FAQs Q. Speaker system enclosures must be well sealed for identical reasons.

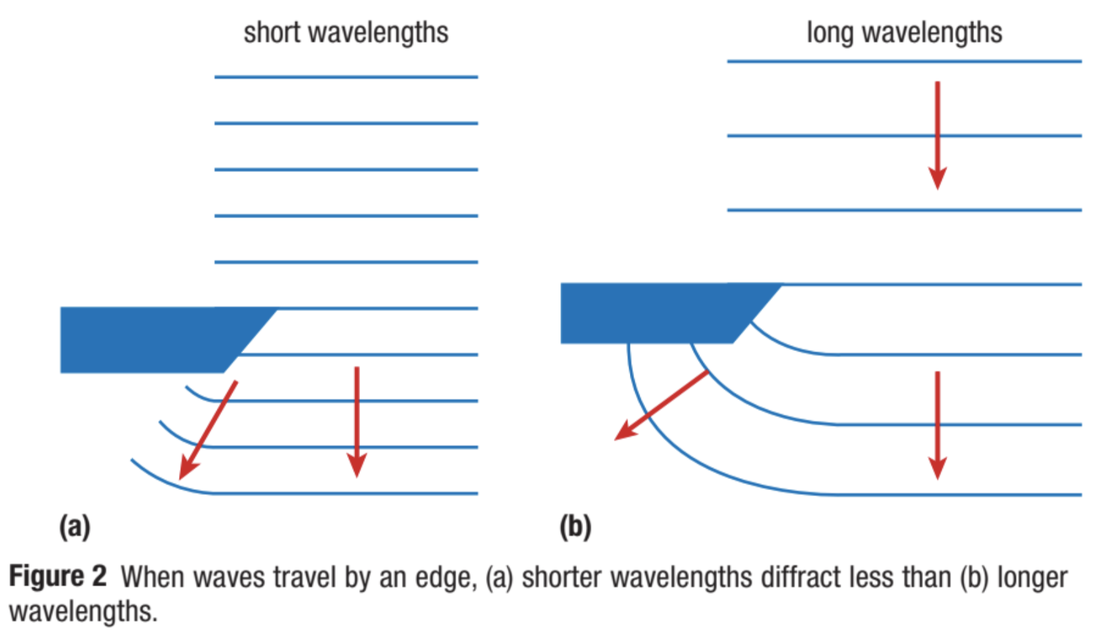
It’s amazing how much noise gets go in via a small crack. Since any holes enable noise from the outside to propagate out in the room, effective silencing necessitates a well-sealed space. Apart from being capable to listen to the noise when standing beyond the room, this extending out of sound waves has implications for soundproofing a room. This diffraction property has a lot of repercussions. Will we be capable to catch the voice if the person who is shouting stand behind a giant tree and yell with the same strength? Yeah, so why do the sound isn’t obstructed if a massive tree is in the way? The reasoning for this is that sound passes and hits our ear via the diffraction phenomenon.īecause the same process that enables rays to curve about barriers also allows them to expand out through tiny holes, one might think of diffraction as having a contradictory character. We are capable to catch the voice if it is said out loud. The lunar corona is the moon’s ring, whereas the solar corona is the sun’s ring. The ‘ring’ of light that encircles the sun or moon is known as the corona. The term corona refers to the brightness circle that develops around the sun or moon following sunlight or moonlight is diffracted by microscopic humidity or ice particles. Conversely, if a small cloud covering is present between the viewer and the moon, the diffraction and dispersion of the moonlight results in an illumination that is brighter in comparison to the actual. The illumination we observe originating from the moon on a cloudless sky, for instance, is coming directly from the moon. The light that goes via the fog droplets is diffracted and diffused when the gap among the droplets is comparable to the wavelength of visible light. Such a curving of a water wave is another example of diffraction. The water wave curves on both sides of the slot. Whenever a lake’s moving water comes into contact with a tiny slit, it is likely to interrupt its usual movement. If the spacing width is roughly the equivalent to the wavelength, the most diffraction occurs. The degree of diffraction increases as the wavelength of the wave increases. Image credit: Snappy goat Water passing from a small gapĭiffraction occurs when water passes out via a hole and is scattered out.
All conceivable diffraction maxima from the dust will be identified if the observation angle is consistently varied. Once an X-ray source is focused on dust with arbitrarily aligned crystallites, the ray will observe all potential inter- atomic surfaces.

Most materials, on the other hand, are polycrystalline aggregates or powders, which are made up of numerous small crystallites in all conceivable configurations. The type and configuration of particles in the lattice arrangement impact the intensity of diffracted waves. The accessible diffraction patterns are determined by the magnitude and shape of the material’s unit cell. That’s the diffraction mechanism.īragg’s Law, n\lambda =2dsin\Theta, describes the diffraction of X-rays using crystals (theta). The dispersed X-rays interact constructively and destructively in substances having uniform organization (i.e. The microscopic faces of the crystalline operate on the X rays in the same precise way as an uniformly controlled grating operates on a light beam.Īs a monochromatic X-ray source engages with a target surface, the dispersion of those X-rays through atoms inside the target surface is the dominating effect. Image credit: Snappy goat X ray diffraction:īecause of their uniform spacing, the atoms of a crystal produce an interference pattern of the ray included in an entering wave of X rays in X-ray diffraction.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
